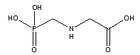
Glyphosate (N-(phosphonomethyl) glycine) is a non-selective systemic herbicide, absorbed through the leaves, injected into the bole, or applied to the stump of a tree, used to kill weeds, especially perennials and broadcast or used in the cut-stump treatment as a forestry herbicide. Some crops have been genetically engineered to be resistant to it.
Biochemistry
Glyphosate kills plants by inhibiting the enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS), which catalyzes the reaction of shikimate-3-phosphate (S3P) and phosphoenolpyruvate to form 5-enolpyruvyl-shikimate-3-phosphate (ESP). ESP is subsequently dephosphorylated to chorismate, an essential precursor in plants for the aromatic amino acids: phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan. These amino acids are used as building blocks in peptides, and to produce secondary metabolites such as folates, ubiquinones and naphthoquinone. The shikimate pathway is not present in animals, which instead obtain aromatic amino acids from their diet. Glyphosate has also been shown to inhibit other plant enzymes and also has been found to affect animal enzymes.
Biochemistry
Glyphosate kills plants by inhibiting the enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS), which catalyzes the reaction of shikimate-3-phosphate (S3P) and phosphoenolpyruvate to form 5-enolpyruvyl-shikimate-3-phosphate (ESP). ESP is subsequently dephosphorylated to chorismate, an essential precursor in plants for the aromatic amino acids: phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan. These amino acids are used as building blocks in peptides, and to produce secondary metabolites such as folates, ubiquinones and naphthoquinone. The shikimate pathway is not present in animals, which instead obtain aromatic amino acids from their diet. Glyphosate has also been shown to inhibit other plant enzymes and also has been found to affect animal enzymes.
